Http Header Management
From Joomla! Documentation
How to Use the New HTTP Header Management in Joomla 4.0
As of Joomla 4.0, Joomla introduced an HTTP Header Management System. This System is designed to help site owners to configure the HTTP Security Headers from the Backend
In this tutorial, you will find information on how to set up this new system on your site.
Plugin[edit]
System - HTTP Headers (plg_system_httpheaders)[edit]
Navigate to System → Plugins → System - HTTP Headers to access the plugin configuration.
Plugin Configuration[edit]
From this page you can choose to enable the headers written to the server configuration files (.htaccess and web.config) and configure whether the following HTTP headers are enabled
Using the Force Header form you can also force the following headers with its values:
- Strict-Transport-Security
- Content-Security-Policy
- Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only
- Expect-CT
- Feature-Policy & Permissions-Policy
- Report-to
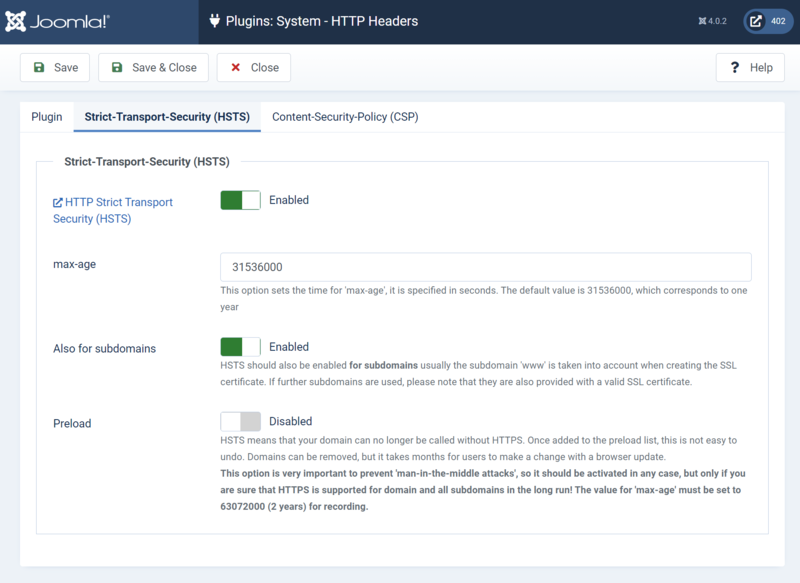
Strict-Transport-Security (HSTS) Configuration[edit]
From this page you can choose to enable the Strict-Transport-Security (HSTS) header as well as configure the max-age value, whether subdomains should be included and whether you want to be added to the browsers Preload List.
Content-Security-Policy (CSP) Configuration[edit]
From this page you can choose to enable and configure the Content-Security-Policy (CSP) header set by the plugin.
Once enabled you can set the client where you want to enforce the configured CSP, allowing you to specify site, administrator or both.
The following settings need a bit more explanation, that's also the reason there are additional descriptions on all of them.
The final option called Add Directive allows you to configure the allowlist per directive as you need them. For example the directive script-src where the option Value you enter the origins you want to allow to load scripts from.
Notes[edit]
When you have configured some HTTP Security Headers directly on the server, our tooling might create double entries.
Check the output of your HTTP Headers after configuring in the browser console. In Google Chrome: Inspect > Network > the output under Headers. You can than disable the headers that cause double entries. Also check the console of your browser for possible errors.
Extension Developers[edit]
As you might know the big security advantage concerning Content Security Policy jumps in when we can use the Header to block all inline JavaScript and inline CSS affecting for example JavaScript event handlers via HTML attributes. With this browser protection enabled we will block inline JavaScript and inline CSS usage also for your extensions. That protection is not enabled by default but can be enabled by your users.
For 4.0 it is recommended to get the frontend of your extension running with strict Content Security Policy enabled. For 4.1 compatibility it is recommended that this also applies to your backend.
It is still a requirement to have inline JavaScript and CSS. For that reason we have implemented nonce and hash support into our Document APIs. When you use them the core will make sure they are whitelisted but we will still block anything malicious to protect our sites.
Important Notes for Extension Developers[edit]
Starting with Joomla 4.0, Content Security Policy:
- is shipped by the core
- is disabled by default
- can be enabled by your users
- it is strongly recommended that your extension frontend works with 4.0 with Content Security Policy enabled
- it is recommended that your extension backend works with 4.1 with Content Security Policy enabled
With strict Content Security Policy enabled the following features will be blocked:
- the execution of JavaScript via the HTML event handlers (onXXX handlers like onClick and similar)
- the execution of in-page JavaScript not passed to the page via the Document API
- the execution of JavaScript code injected into DOM APIs such as eval()
- the usage of inline in-page CSS not passed to the page via the Document API
- the usage of inline CSS using the HTML style attribute
To get your extensions to work even with strict Content Security Policy enabled, use the Document API to apply your inline JavaScript and CSS. Check the examples below.
Adding JavaScript Using the Joomla API[edit]
use Joomla\CMS\Factory;
/** @var Joomla\CMS\WebAsset\WebAssetManager $wa */
$wa = Factory::getApplication()->getDocument()->getWebAssetManager();
// Add JavaScript from URL
$wa->registerAndUseScript('com_example.sample', 'https://example.org/sample.js', [], ['defer' => true]);
// Add inline JavaScript
$wa->addInlineScript('
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function(event) {
alert("An inline JavaScript Declaration");
});
');Adding CSS Using the Joomla API[edit]
use Joomla\CMS\Factory;
/** @var Joomla\CMS\WebAsset\WebAssetManager $wa */
$wa = Factory::getApplication()->getDocument()->getWebAssetManager();
// Add Style from URL
$wa->registerAndUseStyle('com_example.sample', 'https://example.org/sample.css');
// Add inline Style
$wa->addInlineStyle('
body {
background: #00ff00;
color: rgb(0,0,255);
}
');More details can be found here: Adding JavaScript and CSS to the page